how to remove some to upload on git using push

Git is an important part of daily programming (specially if y'all're working with a team) and is widely used in the software manufacture.
Since there are many various commands you can use, mastering Git takes fourth dimension. Just some commands are used more frequently (some daily). So in this post, I will share and explicate the x nigh used Git commands that every programmer should know.
Note: To sympathize this article, you lot demand to know the basics of Git.
ane. Git clone
Git clone is a control for downloading existing source code from a remote repository (like Github, for example). In other words, Git clone basically makes an identical copy of the latest version of a project in a repository and saves it to your computer.
There are a couple of means to download the source code, merely mostly I adopt the clone with https way:
git clone <https://name-of-the-repository-link> For example, if nosotros want to download a project from Github, all we demand to exercise is click on the greenish button (clone or download), copy the URL in the box and paste it later on the git clone command that I've shown right above.
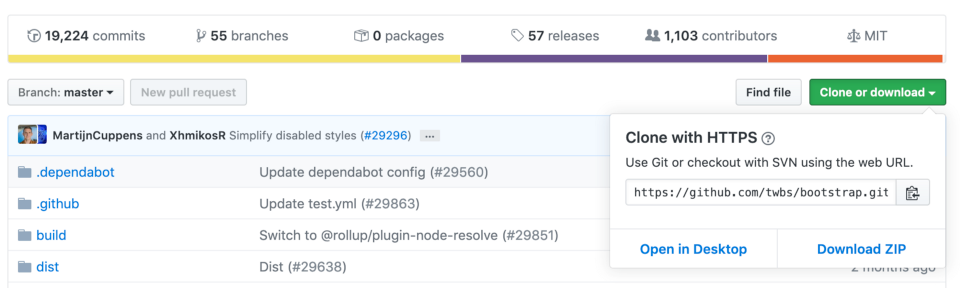
This volition make a copy of the project to your local workspace so yous tin can start working with it.
2. Git branch
Branches are highly of import in the git world. Past using branches, several developers are able to work in parallel on the same project simultaneously. We can use the git branch command for creating, list and deleting branches.
Creating a new branch:
git branch <branch-name> This control will create a branch locally. To push the new branch into the remote repository, y'all need to use the post-obit command:
git push button -u <remote> <co-operative-proper noun> Viewing branches:
git co-operative or git co-operative --list Deleting a branch:
git branch -d <branch-name> 3. Git checkout
This is also ane of the about used Git commands. To work in a co-operative, outset y'all need to switch to information technology. We use git checkout mostly for switching from one co-operative to another. We can also use it for checking out files and commits.
git checkout <proper noun-of-your-branch> There are some steps you need to follow for successfully switching betwixt branches:
- The changes in your current branch must be committed or stashed before you switch
- The branch you want to check out should exist in your local
At that place is also a shortcut command that allows you to create and switch to a branch at the same time:
git checkout -b <proper noun-of-your-branch> This command creates a new co-operative in your local (-b stands for branch) and checks the branch out to new right after it has been created.
4. Git status
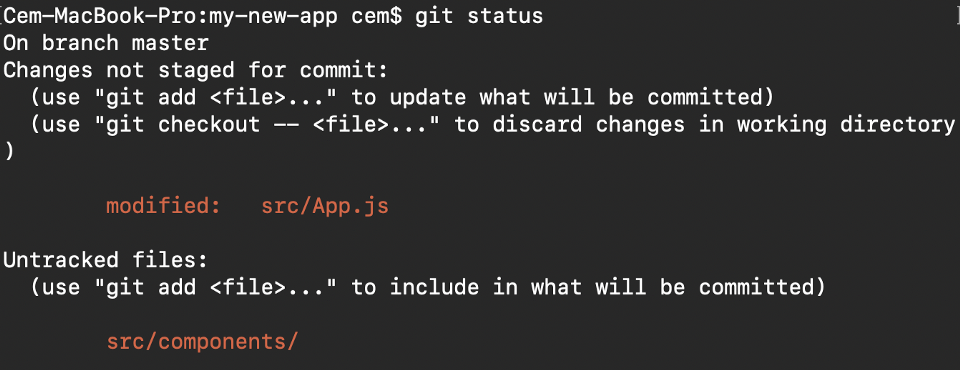
The Git status command gives us all the necessary information about the electric current co-operative.
git status We can gather information like:
- Whether the electric current branch is up to engagement
- Whether there is annihilation to commit, push or pull
- Whether there are files staged, unstaged or untracked
- Whether there are files created, modified or deleted
5. Git add
When we create, modify or delete a file, these changes will happen in our local and won't be included in the side by side commit (unless we alter the configurations).
We demand to use the git add command to include the changes of a file(southward) into our next commit.
To add together a single file:
git add <file> To add everything at in one case:
git add -A When you visit the screenshot to a higher place in the 4th section, you volition see that there are file names that are red - this means that they're unstaged files. The unstaged files won't be included in your commits.
To include them, we need to use git add:
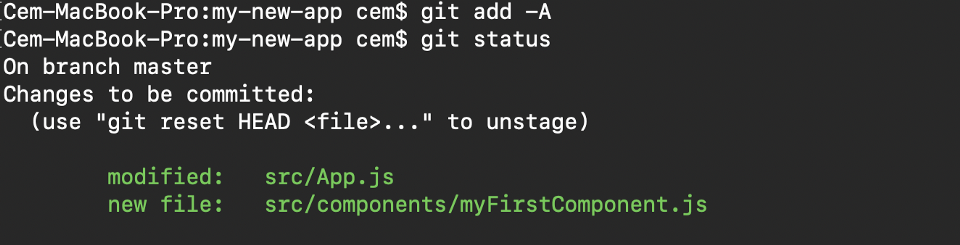
Important: The git add control doesn't alter the repository and the changes are non saved until we use git commit.
six. Git commit
This is maybe the most-used command of Git. Once we reach a certain point in evolution, nosotros want to relieve our changes (maybe after a specific task or consequence).
Git commit is like setting a checkpoint in the evolution procedure which you can go back to later on if needed.
We also need to write a short message to explicate what we have developed or changed in the source code.
git commit -m "commit message" Important: Git commit saves your changes only locally.
7. Git button
After committing your changes, the next thing you desire to exercise is send your changes to the remote server. Git push button uploads your commits to the remote repository.
git push <remote> <co-operative-name> However, if your co-operative is newly created, and so you as well need to upload the branch with the following command:
git push button --set-upstream <remote> <proper noun-of-your-branch> or
git push -u origin <branch_name> Important: Git push only uploads changes that are committed.
8. Git pull
The git pull command is used to get updates from the remote repo. This command is a combination of git fetch and git merge which means that, when we utilise git pull, it gets the updates from remote repository (git fetch) and immediately applies the latest changes in your local (git merge).
git pull <remote> This operation may cause conflicts that you need to solve manually.
ix. Git revert
Sometimes we need to undo the changes that we've made. In that location are various ways to undo our changes locally or remotely (depends on what we need), but we must carefully use these commands to avoid unwanted deletions.
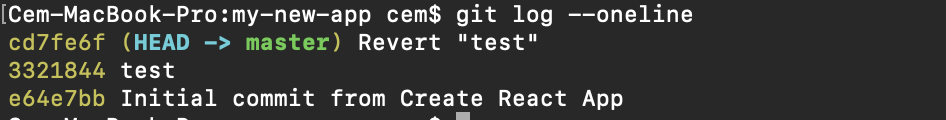
A safer style that we can disengage our commits is by using git revert. To see our commit history, first nosotros need to use git log -- oneline:

Then we simply need to specify the hash code next to our commit that we would like to disengage:
git revert 3321844 Later this, y'all will encounter a screen like beneath - but press shift + q to get out:
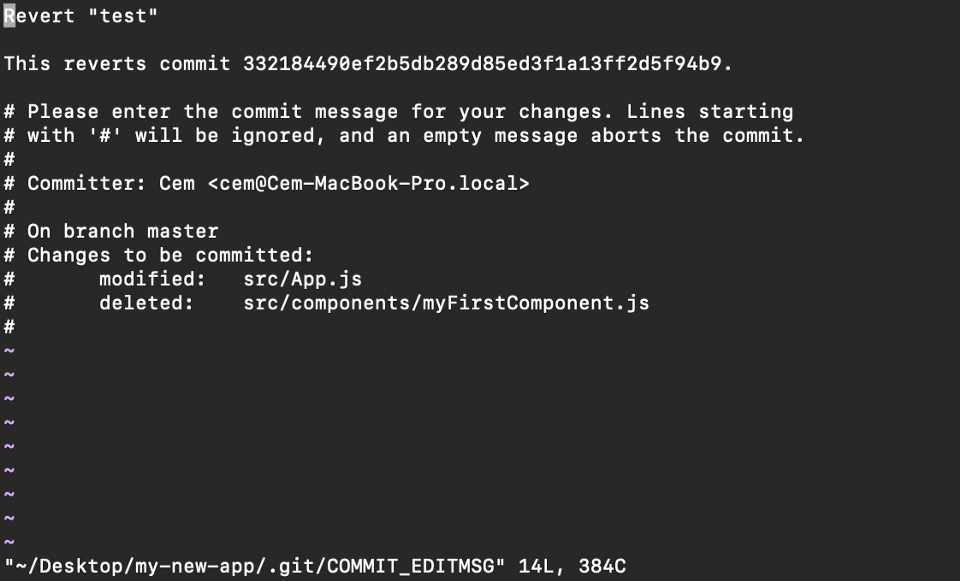
The Git revert control will disengage the given commit, but will create a new commit without deleting the older ane:
The advantage of using git revert is that it doesn't impact the commit history. This means that you can still run across all of the commits in your history, even the reverted ones.
Another safety mensurate here is that everything happens in our local arrangement unless nosotros button them to the remote repo. That'south why git revert is safer to utilize and is the preferred way to undo our commits.
10. Git merge
When yous've completed evolution in your co-operative and everything works fine, the final stride is merging the co-operative with the parent branch (dev or principal). This is done with the git merge command.
Git merge basically integrates your feature branch with all of its commits back to the dev (or chief) branch. Information technology's important to remember that you first need to be on the specific branch that yous want to merge with your feature branch.
For instance, when yous want to merge your characteristic co-operative into the dev branch:
First you should switch to the dev branch:
git checkout dev Before merging, you should update your local dev branch:
git fetch Finally, yous can merge your feature branch into dev:
git merge <branch-name> Hint: Make certain your dev branch has the latest version earlier y'all merge your branches, otherwise you may face conflicts or other unwanted problems.
So these are my 10 most-used git commands that I come across in my daily programming. There are many more things to acquire most Git and I will explain them later in separate articles.
If yous want to learn more about web development, feel free to follow me on Youtube !
Thank you for reading!
Larn to code for free. freeCodeCamp'due south open up source curriculum has helped more than twoscore,000 people go jobs as developers. Get started
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/10-important-git-commands-that-every-developer-should-know/
0 Response to "how to remove some to upload on git using push"
Post a Comment